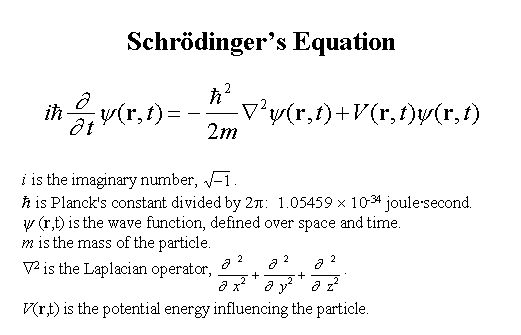Every quantum particle is characterized by a wave function. In 1925 Erwin Schrödinger developed the differential equation which describes the evolution of those wave functions. By using Schrödinger's equation scientists can find the wave function which solves a particular problem in quantum mechanics. Unfortunately, it is usually impossible to find an exact solution to the equation, so certain assumptions are used in order to obtain an approximate answer for the particular problem.